Resuscitation Triangle Roles: An Informational Guide
The Concept of Resuscitation Triangle Roles
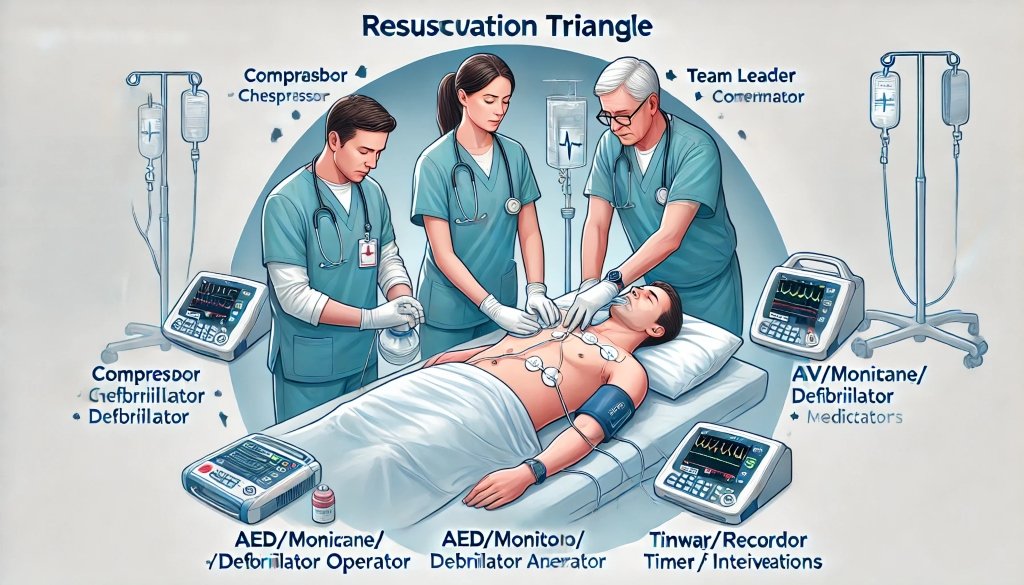
The resuscitation triangle consists of three critical roles that are essential for effective resuscitation: Compressor, AED/Monitor/Defibrillator, and Airway/Ventilator. Additionally, there are leadership roles that support and coordinate the efforts of the hands-on team members. This structured approach ensures that each team member has a clear, defined responsibility, minimizing confusion and maximizing efficiency during a resuscitation attempt.
Key Roles in the Resuscitation Triangle
1. Compressor
Responsibilities:
- Perform high-quality chest compressions to maintain blood circulation.
- Alternate with the AED/Monitor/Defibrillator every two minutes or five cycles to prevent fatigue.
- Continuously assess the patient’s status and adjust the depth and rate of compressions as needed.
The Compressor plays a crucial role in maintaining blood flow to vital organs. Effective compressions are vital, as they help sustain the patient’s chances of survival until advanced interventions can be applied.
2. AED/Monitor/Defibrillator
Responsibilities:
- Operate the AED or defibrillator, delivering shocks as necessary.
- Monitor the patient’s heart rhythm and communicate findings to the team leader.
- Alternate with the Compressor to ensure both team members remain effective and alert.
This role is essential for identifying and correcting life-threatening arrhythmias through defibrillation. Proper use of the AED and continuous monitoring are critical for the timely administration of electrical therapy.
3. Airway/Ventilator
Responsibilities:
- Ensure the patient’s airway is open and clear.
- Provide ventilation using a bag-valve mask or advanced airway devices.
- Continuously monitor the effectiveness of ventilation and adjust as necessary.
Maintaining a clear airway and providing adequate ventilation are vital to ensure the patient receives enough oxygen. The Airway/Ventilator role is critical for preventing hypoxia and supporting overall resuscitation efforts.
Leadership Roles Supporting the Triangle
1. Team Leader
Responsibilities:
- Assign roles and tasks to team members based on their skills and experience.
- Make critical treatment decisions and provide guidance throughout the resuscitation.
- Ensure clear, closed-loop communication among all team members.
The Team Leader is the central figure who coordinates the efforts of the entire team, ensuring that each role is performed correctly and efficiently. This leadership is crucial for maintaining order and focus during high-stress situations.
2. IV/IO/Medication Administrator
Responsibilities:
- Establish intravenous or intraosseous access for medication administration.
- Administer medications according to ACLS protocols and team leader directives.
- Ensure that IV/IO access remains patent and functional throughout the resuscitation.
Medications can play a significant role in correcting underlying issues during cardiac arrest, and the IV/IO/Medication Administrator ensures that drugs are delivered promptly and correctly.
3. Timer/Recorder
Responsibilities:
- Track the timing of interventions, including compressions, shocks, and medication administration.
- Document all actions taken during the resuscitation for post-event review and quality improvement.
- Communicate timing-related information to the team leader and other members to ensure adherence to protocols.
Accurate timing and documentation are crucial for maintaining the rhythm and flow of resuscitation efforts, ensuring that all interventions are performed at the correct intervals.
Enhancing Team Dynamics
Effective Communication
Clear and concise communication is fundamental in a high-performance resuscitation team. Closed-loop communication ensures that instructions are understood and executed correctly, reducing the risk of errors and miscommunication.
Continuous Training
Regular training and simulation exercises help team members stay proficient in their roles and improve their ability to work together seamlessly. This preparation is essential for maintaining high standards of care during real-life resuscitations.
Adaptability
Each resuscitation event is unique, and teams must be able to adapt quickly to changing circumstances. Flexibility and the ability to improvise while adhering to core principles and protocols are key characteristics of successful resuscitation teams.
The resuscitation triangle roles provide a structured approach to managing cardiac emergencies, ensuring that all critical tasks are covered and performed effectively. By understanding and executing these roles, healthcare providers can significantly improve patient outcomes during resuscitation efforts. Continuous training, clear communication, and strong leadership are essential components of a high-performance resuscitation team, making the difference between life and death in emergency situations.
For further reading and more detailed guidelines on resuscitation triangle roles, consult professional training resources and certification courses in Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS).